In June 2023, the first wave of Draft RTS (Regulatory Technical Standards) and ITS (Implementing Technical Standard) was published by the European Supervisory Authorities. The objective of these additional Policy Products is to provide detailed specifications and guidelines on how certain provisions in the basic legislative Act should be implemented across the EU.
The first batch of Policy Products are Draft and have been published for consultation consists of:
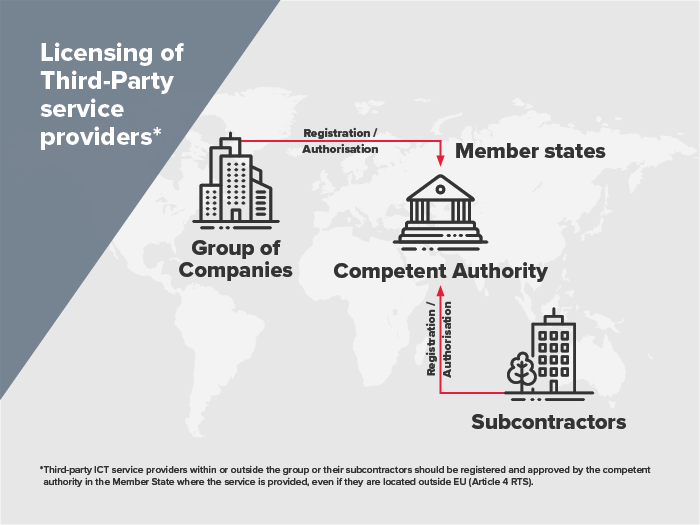
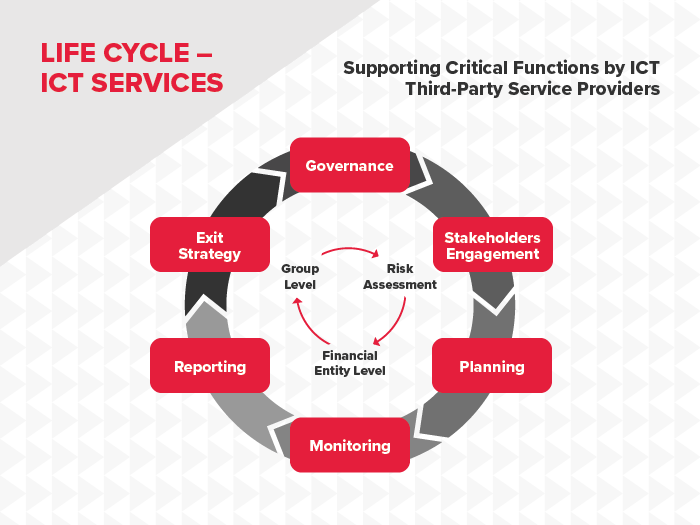
- RTS to specify the policy on ICT services performed by ICT third-party providers (Article 28(10))
- RTS on criteria for the classification of ICT-related incidents (Article 18(3))
- ITS to establish the templates for the register of information (Art.28(9))
- RTS on ICT risk management framework (Article 15) and RTS on simplified ICT risk management framework (Article 16(3))