The AI Act is recognised as the world's first comprehensive regulatory framework specifically addressing the threats and risks associated with AI tools and technology. Think for example about biased decision-making in recruitment, opaque credit scoring systems, unsafe applications in healthcare, or manipulative use of generative AI.
The key objective of this act is to promote safe practices of AI, protect fundamental privacy rights, and promote innovation in a controlled manner. The act establishes a clear framework that includes obligations for both developers and users of AI systems. This includes conducting risk assessments, ensuring the quality of data, and maintaining thorough documentation.
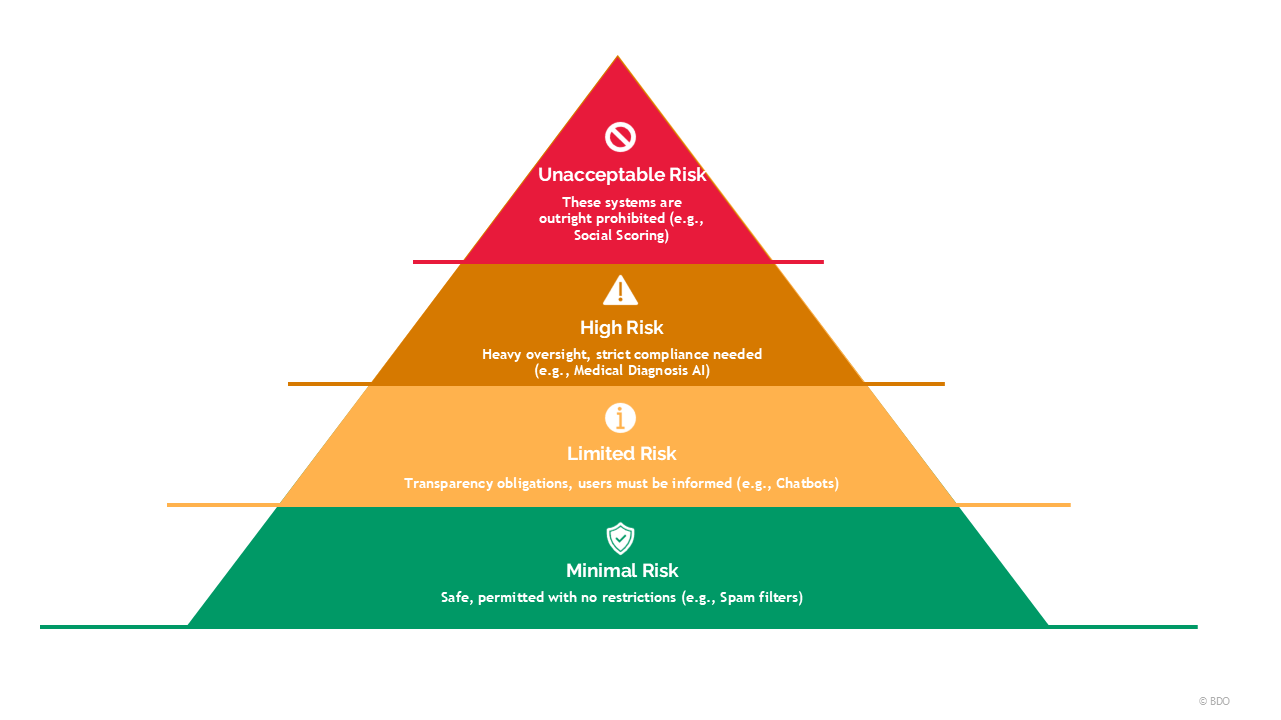
This piece of legislation aims to categorise AI systems into distinct risk levels based on
- the potential impact of an individual’s rights and safety,
- the context in which the system is deployed,
- the level of human interaction and control,
- and the potential for biased results or the ability to manipulate human behaviours.
The act distinguishes this through four key risk levels: Unacceptable, High, Limited, and Minimal. AI systems with unacceptable risk will be banned, while high-risk systems will face stringent requirements regarding transparency, accountability, and safety.