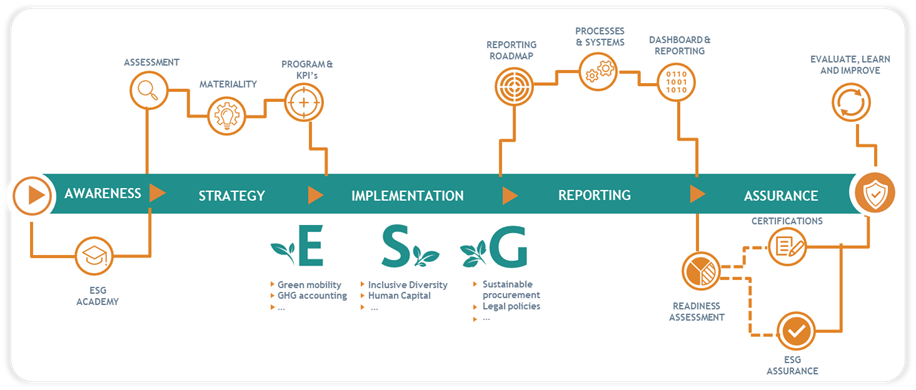
What is sustainability/ESG anyway?
The overarching concept of sustainability refers to the extent to which we can meet our needs without depleting natural resources or causing harmful environmental impacts. At the same time, sustainability focuses on promoting wellbeing in our society.
Companies play a crucial role in promoting sustainability. They can integrate corporate sustainability into their business strategy and daily operations to both reduce the negative impact and optimise the positive impact.
When doing so, it is important to approach this concept from all angles, in particular from an Environmental (environment), Social (social impact) and Governance (good governance) perspective. Examples of this ESG perspective include reducing carbon emissions, ensuring healthy and safe working conditions for employees and ensuring transparent reporting rules.
Of course, as a company, you don’t have to work on every possible sustainability issue. BDO advises entrepreneurs to make targeted choices in this area.
The broad business case of sustainable business
Sustainable business is often linked to thresholds/challenges such as:
- “It is just a cost, it makes no (or almost no) profit.”
- “My customer doesn’t want to pay for this.”
- “As long as I have to compete with countries like China, there is no room for ESG in my business.”
Therefore, it is important to understand the “broad business case” of sustainable business. Companies that move from ad hoc initiatives (such as installing solar panels or setting up a wellbeing policy) to integrating ESG into their corporate strategy (integrating ESG in the decision-making process of all departments at all levels) do so with the belief that this will create value and manage risk for their business. The benefits for companies are diverse and differ depending on business context, ambitions and sector, among others:
- Innovation and competitive advantage: sustainability can drive innovation. It encourages and - in some situations - even forces you as a company to develop new, environmentally friendly technologies and solutions. Just think of the many “green” variants of existing products and new solutions. Sustainable business practices can open doors to growing markets of environmentally conscious consumers. This can give you a competitive advantage and a higher market share in a rapidly changing market and economic environment.
- Cost savings: sustainable practices can lead to lower operational costs. Think, for example, about waste reduction, lower energy consumption or reusing resources and materials. In other words, resource efficiency can reduce operational costs in your organisation and increase profitability.
- Compliance with regulations and standards: policymakers are launching more and more initiatives to encourage sustainable entrepreneurship, from explicitly banning things (see rules on CO2 emissions and nitrogen, among others), more transparency (reporting sustainability performance) or rewarding environmentally friendly investments through premiums and subsidies. If not properly prepared, high costs may be involved in complying last minute, stranded assets and fines for non-compliance with sustainability regulations or standards.
- Access to capital: investors are increasingly integrating ESG criteria into their decision-making process. Do you score high on sustainability criteria as a company? Then you get easier access to capital and stand a chance of getting more favourable financing terms. In addition, ESG criteria are increasingly being integrated into valuation exercises by private equity players, among others. So you can get a higher valuation as a company by integrating ESG into your operations.
- Risk management: integrating sustainability into your corporate strategy helps you to make your operations future-proof. You can do so by creating sustainable value and identifying and managing risks related to regulatory, reputational and supply chain issues, among others. Examples of risks include the impact of climate change on the supply chain (physical risks) or fines for non-compliance with sustainability standards (transition risks).
- A strong (or stronger) employer brand: research shows that younger generations (Generation Z) prefer employers with a strong focus on sustainable business. So companies that embrace sustainability are more successful at attracting and retaining talented employees. Not insignificant in these times of labour market tightness...
Keep tough challenges in mind
Besides the broad business case, companies also face challenges to integrate sustainability into their business strategy. A selection of potential challenges for companies to consider:
- Cost and investment: implementing sustainable practices may initially involve high costs, such as upgrading production methods, replacing outdated equipment or investing in renewable energy sources. Are you prepared, as a company, to make these investments before reaping the long-term benefits?
- Regulatory and compliance: sustainability often goes hand in hand with stricter regulations, especially in terms of environment and working conditions. As a company, you have to adapt to new rules of the game, which can bring legal and operational challenges.
- A complex supply chain: ensuring sustainability throughout the supply chain can be complicated, especially for global companies. It requires close monitoring and collaboration with suppliers, which can lead to additional efforts and costs.
- An adapted corporate culture: sustainable business often requires a change in corporate culture and mindset. Involving your employees in this change process can take time and investment to get everyone on the same page.
.jpg)
.jpg)